Application of the Results
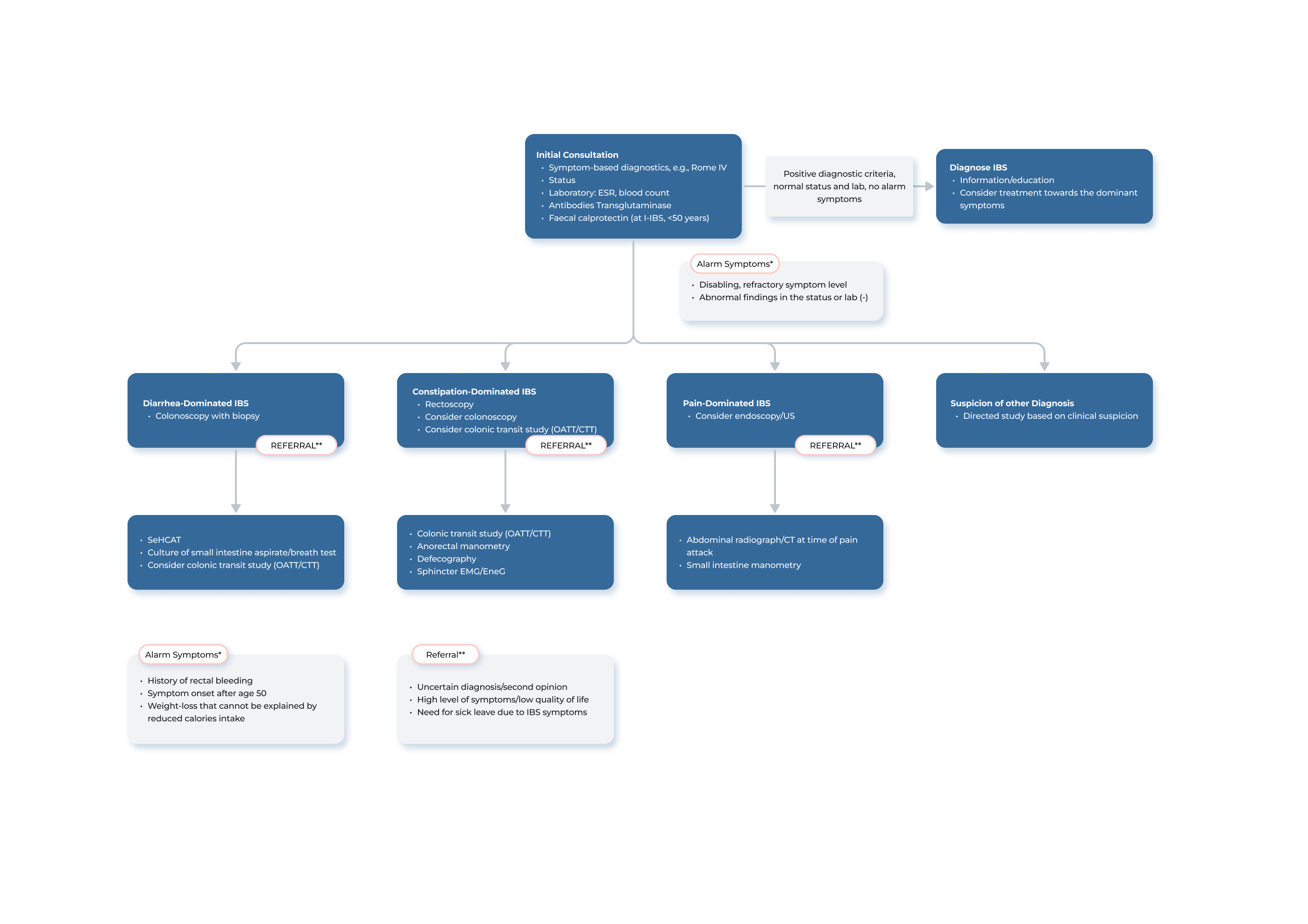
Upon completion of the CTT measurement, it is important to review the results with the patient and present the obtained transit profile. The transit profile should in general be interpreted in the context of the patient´s reported symptoms.
The following is a suggested approach for utilizing the results of a colonic transit test with Transit-Pellets radiopaque markers1, 2, 3. It is important to note that the ultimate decision regarding the interpretation and application of these results, as well as the course of subsequent treatment, should be made by the treating physician.
- If the results indicate that the overall transit is normal, patient education, dietary guidance, and/or osmotic laxatives are often sufficient. If dyssynergic defecation is present, biofeedback therapy may be recommended
- If the results show that the colonic transit is delayed, intensification of constipation therapy, including adjustments to laxative treatment and the use of motility-stimulating medications, may be necessary
- In slow-transit constipation, radiopaque markers are typically retained throughout the entire colon, while concentration of markers in the caecum and ascending colon, may indicate colonic inertia
- If the patient experiences severe constipation but the transit time is completely normal, it is possible that altered sensitivity, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), is present and therapy should be tailored accordingly
- If a patient´s colonic transit test reveals a delayed transit time in the recto-sigmoid region, it may be indicative of an outlet obstruction disorder. In such cases, further investigation may be required, such as balloon expulsion test or ano-rectal manometry may be needed to determine the functional or structural cause of evacuatory dysfunction
- If a patient is experiencing chronic diarrhoea and the results shows rapid transit in the distal colon, it may be indicative of bile acid diarrhoea
For further perspective on factors to take into account when conducting a colonic transit test utilizing the Transit-Pellets method and Transit-Pellets radiopaque markers, we recommended visiting the section Why assess Colonic Transit Time (CTT) with the Transit-Pellet single X-ray method?
- Keller, J., Bassotti, G., Clarke, J., et al. (2018). EXPERT CONSENCUS DOCUMENT. Advances in the diagnosis and classification of gastric and intestinal motility disorders [electronic version]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol., Vol. 15(5), 291-308.
- 0020 Clinical Evaluation Report – Transit-Pellets ver08 (Internal Document). November 2023.
- EM 23-003 The Disordered Bowel – Transit-Pellets are useful in both ends of the spectrum ver01 (Internal Document). June 2023.